
A Food and Beverage Service course typically covers the essential skills, knowledge, and techniques required for working in the food and beverage industry. This includes both theoretical aspects and practical training in the various components of food and drink service. Here’s a general course summary:
1. Introduction to Food and Beverage Service
- Overview of the Industry: Understanding the food and beverage service sector, including types of establishments (e.g., restaurants, hotels, catering).
- Roles and Responsibilities: Key positions in food and beverage service (e.g., servers, bartenders, chefs, managers) and their duties.
2. Types of Service
- Table Service: Learning the different styles of table service, such as French service, Russian service, American service, and English service.
- Buffet Service: Setting up and serving food at buffets, managing self-service areas.
- Room Service: Techniques for delivering food and beverages to guests in hotel rooms.
- Bar Service: How to serve drinks at a bar, understand different drink categories, and manage bar inventory.
3. Food and Beverage Menu Knowledge
- Menu Types and Layouts: Understanding different types of menus (à la carte, table d’hôte, fixed, and seasonal menus) and how they are structured.
- Menu Planning: Designing and planning a menu considering factors like cost, variety, and nutrition.
- Food and Beverage Pairing: Knowledge of pairing wines, beverages, and food to enhance guest experience.
4. Service Equipment and Tools
- Table Settings: How to properly set tables for various types of services (formal, informal, buffet).
- Service Utensils and Glassware: Understanding the proper use of different utensils, glassware, and crockery for serving various types of food and drinks.
- Serving Tools: Training in using service tools like trays, trolleys, and beverage dispensers.
5. Customer Service and Etiquette
- Guest Interaction: Developing effective communication skills with guests, ensuring a positive experience.
- Professional Etiquette: Understanding the importance of appearance, manners, and respectful behavior in a service environment.
- Handling Complaints: Techniques for managing customer complaints and feedback to ensure guest satisfaction.
6. Food Safety and Hygiene
- Food Safety Standards: Understanding hygiene regulations, food handling, and storage procedures to prevent contamination.
- Personal Hygiene: Maintaining personal cleanliness and ensuring staff adhere to hygiene standards.
- Cleaning and Sanitization: Techniques for properly cleaning service areas and equipment.
7. Alcoholic and Non-Alcoholic Beverages
- Types of Beverages: Detailed knowledge of alcoholic beverages (wine, beer, spirits) and non-alcoholic beverages (juices, sodas, coffee, tea).
- Beverage Service: Techniques for serving and presenting beverages appropriately, including bartending skills, wine service, and cocktail preparation.
- Responsible Alcohol Service: Laws and best practices for serving alcohol responsibly, including checking IDs, handling intoxicated guests, and maintaining a safe environment.
8. Sales Techniques
- Up-selling and Cross-selling: How to increase sales by suggesting additional items or premium options to customers.
- Suggestive Selling: Techniques for guiding guests towards certain food or beverage items that will enhance their experience.
9. Bar and Wine Service
- Wine Knowledge: Understanding different types of wines, how to store and serve them, and how to pair wine with food.
- Cocktail Making: Learning the basics of bartending, including common cocktail recipes, mixing techniques, and garnish presentation.
- Bar Management: Techniques for managing a bar, including inventory control, ordering, and organizing drink menus.
10. Service Procedures and Organization
- Service Flow: Understanding the step-by-step process of service from guest arrival to departure, ensuring a smooth dining experience.
- Teamwork and Coordination: The importance of teamwork in the kitchen and front-of-house operations to ensure timely and efficient service.
- POS Systems: Introduction to Point of Sale (POS) systems used for taking orders, processing payments, and managing restaurant operations.
11. Health, Safety, and Legal Aspects
- Health and Safety Regulations: Compliance with local laws regarding food preparation, service, and alcohol licensing.
- Legal Requirements: Understanding the legal aspects of food and beverage service, including labor laws, alcohol service regulations, and customer rights.
12. Trends in the Food and Beverage Industry
- Current Trends: Keeping up with industry trends such as plant-based menus, sustainability, health-conscious dining, and technology integration (e.g., ordering apps, contactless payment).
- Cultural Considerations: Catering to diverse cultural and dietary preferences, understanding allergies, vegetarianism, veganism, and halal/kosher requirements.
13. Career Development
- Building a Career in Food and Beverage Service: Guidance on career opportunities in the food and beverage industry, including advancement from entry-level positions to managerial roles.
- Professional Development: Opportunities for certifications, continuing education, and specialized training in advanced food and beverage service
- Teacher: Admin User
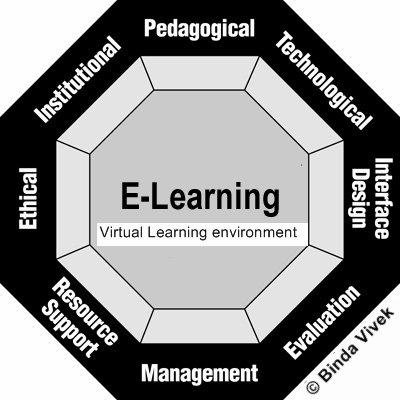
An e-learning resources course typically covers various tools, platforms, and strategies to create, manage, and deliver educational content online. Here's a general summary of the key elements that would be included in such a course:
1. Introduction to E-Learning
- Definition and Importance: Understanding e-learning, its advantages, and the role it plays in modern education and training.
- Types of E-Learning: Asynchronous (self-paced learning), synchronous (live sessions), blended learning (combination of online and in-person), and microlearning.
2. E-Learning Platforms and Tools
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms such as Moodle, Blackboard, and Canvas for organizing and delivering online courses.
- Authoring Tools: Software tools like Articulate Storyline, Adobe Captivate, and H5P for creating interactive e-learning content.
- Video and Audio Tools: Tools for creating and editing instructional videos, podcasts, or webinars (e.g., Camtasia, OBS Studio, Audacity).
- Interactive Tools: Tools for engaging students, such as Kahoot, Quizlet, or Padlet.
3. Content Creation and Design
- Instructional Design Principles: Understanding how to design engaging and effective online courses, focusing on learner-centered strategies.
- Multimedia Integration: Using text, images, videos, and animations effectively in the course material.
- Gamification: Applying game elements like rewards, leaderboards, and challenges to make learning more engaging.
4. Assessment and Evaluation
- Formative vs. Summative Assessment: Techniques for evaluating learners throughout the course and at the end.
- Quizzes and Tests: Best practices for creating meaningful assessments in e-learning courses.
- Analytics and Feedback: Using data and learner feedback to improve course content and delivery.
5. Collaboration and Communication
- Discussion Forums and Social Learning: Tools for peer-to-peer interaction, like forums, wikis, and collaborative document editing.
- Webinars and Virtual Classrooms: Platforms for live online classes and communication, such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Meet.
- Email, Chats, and Messaging Tools: For course announcements and real-time communication.
6. Accessibility and Inclusivity
- Universal Design for Learning (UDL): Ensuring content is accessible to all learners, including those with disabilities.
- Assistive Technologies: Tools that aid learners with disabilities, like screen readers, captioning, and alternative text.
- Language and Cultural Considerations: Creating e-learning resources that cater to a diverse audience.
7. Learning Analytics and Reporting
- Tracking Learner Progress: Understanding and using metrics such as completion rates, engagement levels, and assessment scores.
- Using Data for Course Improvement: Applying insights from analytics to enhance course content and learner engagement.
8. Trends and Future of E-Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) in E-Learning: How AI can personalize learning, automate administrative tasks, and enhance content delivery.
- Mobile Learning (m-Learning): Adapting content for mobile devices to enable learning on the go.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Immersive technologies that create more engaging learning experiences.
9. Best Practices for E-Learning
- Learner Engagement: Strategies for keeping learners motivated and engaged throughout the course.
- Microlearning: Breaking down learning content into bite-sized chunks for easy consumption.
- Continuous Improvement: Collecting feedback, iterating on course designs, and staying up to date with e-learning technologies and trends.
- Teacher: Admin User